Database Entity
Prerequisites
To use a Database Entity, you first need to create a persistable data type. You can make a data type persistable by marking the data type object as persistent. This allows its attributes to be used within a Database Entity step in a function.
How to create a Persistable DataType?
After you create a Data Type and enable Persistence, you can navigate to the Entity tab.
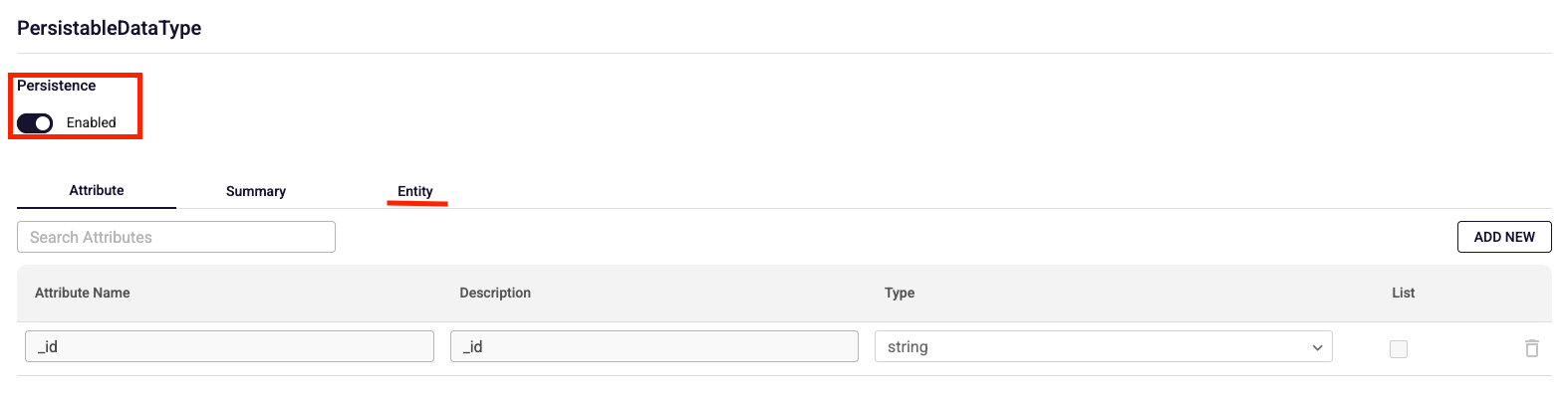
Under the Entity tab, insert, delete, and update queries are automatically generated and cannot be edited. An unchangeable collection name is also created for the corresponding database operations.
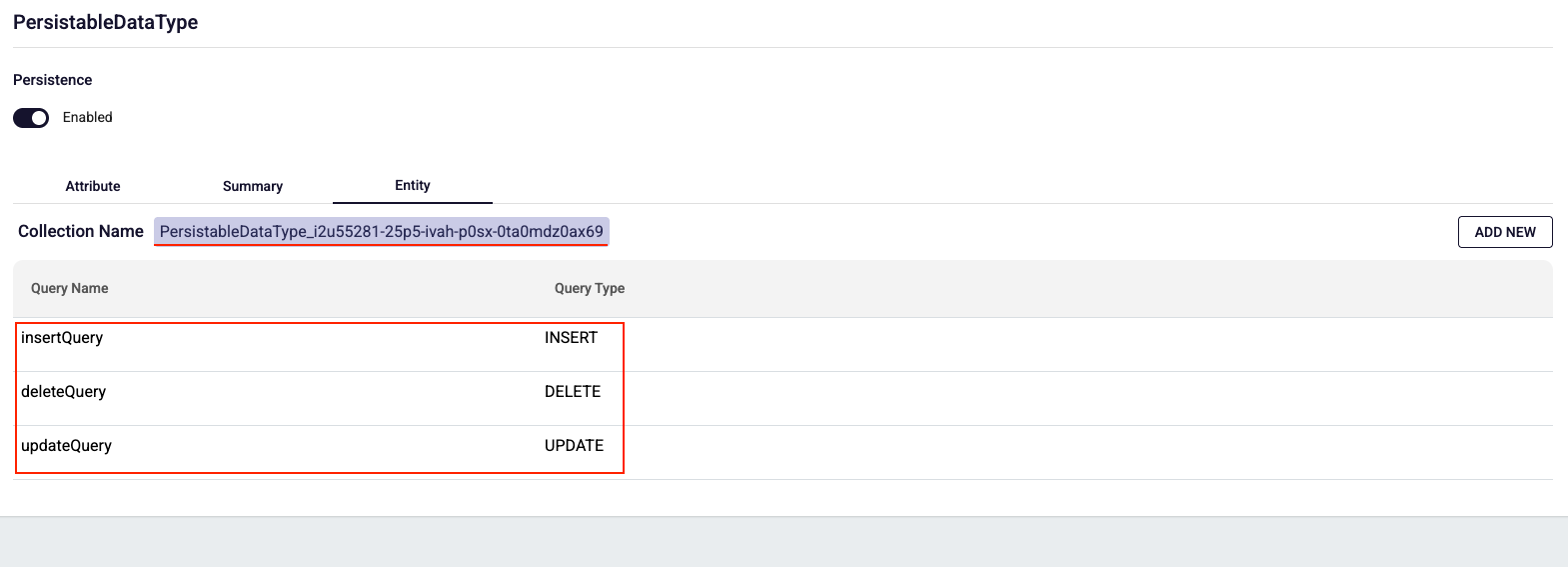
To create a select query, click the Add New button.
How to add new attributes?
In the Attribute tab, you can add new attributes and define their description and type. The attributes you add can then be used in the Entity tab.
How to create a select query?
When creating a new select query, you must provide a Query Name and at least one of the following: Fields or Filter. If you don't provide the required information, the Done button remains inactive and the query cannot be saved.
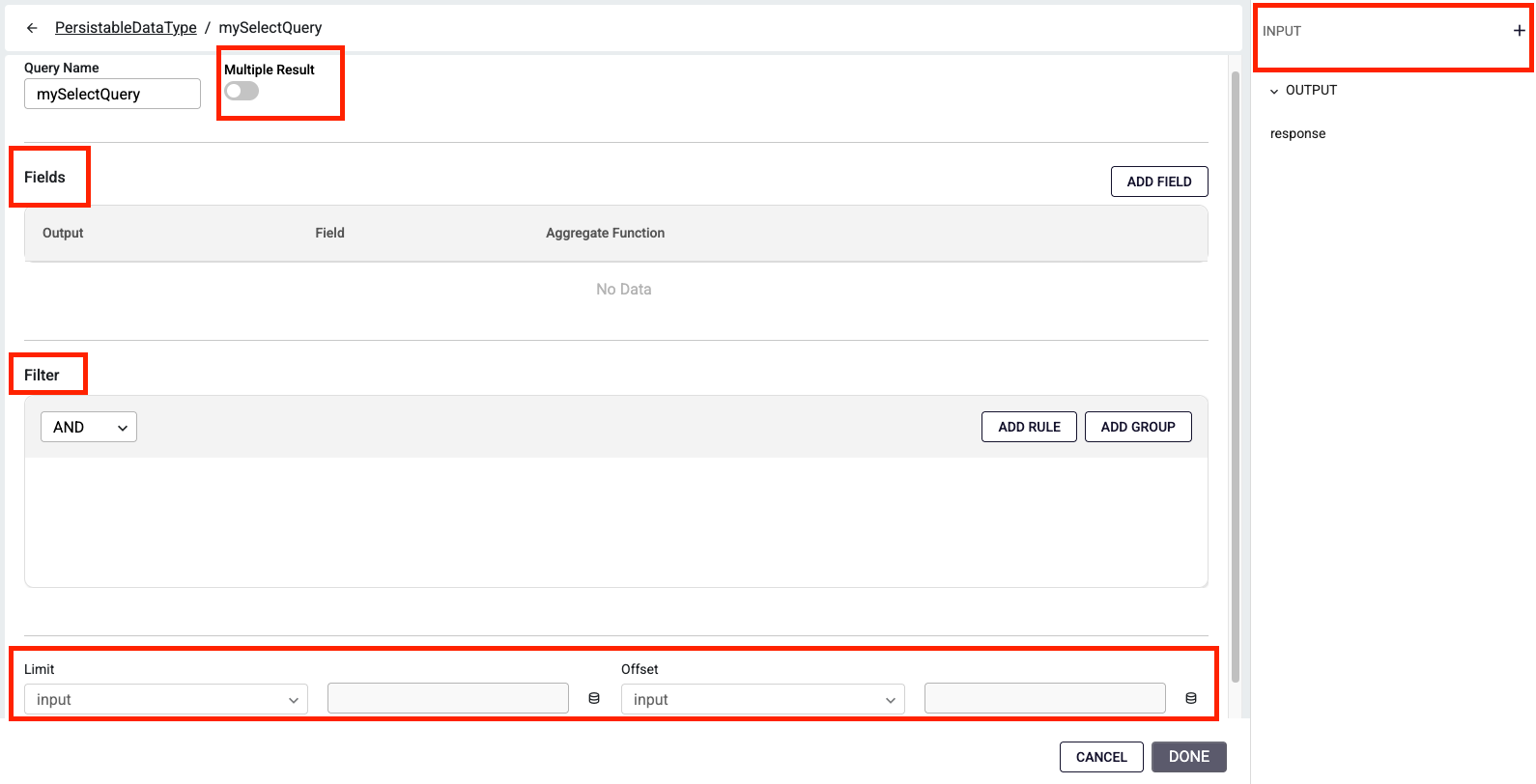
How to use Field Table?
Within a Field column, you can select one of the attributes created in the Attribute tab and apply an appropriate aggregate function.
Sum and Avg can be applied only to data types: number and any.
Min and Max can be applied to data types: number, string, datetime, boolean, and any.
If you select None, no aggregate function is applied, and the field is included in the output as-is.
In the Fields table, you can also define the Output Name, which specifies the alias for the returned value.
How to use Filter Table?
In the Filter section, you can create rules to restrict the returned data. These rules can be combined using logical operators such as AND or OR, allowing you to include only the attributes that match the defined conditions.
When creating a filter, you can define groups of rules. Each group is connected by a logical operator (AND or OR) that applies to all rules and sub-groups within it.
For example, the filter shown in the image would be represented as:
(category = "clothing") AND (amount = "500" OR (customer = "Plateau"))
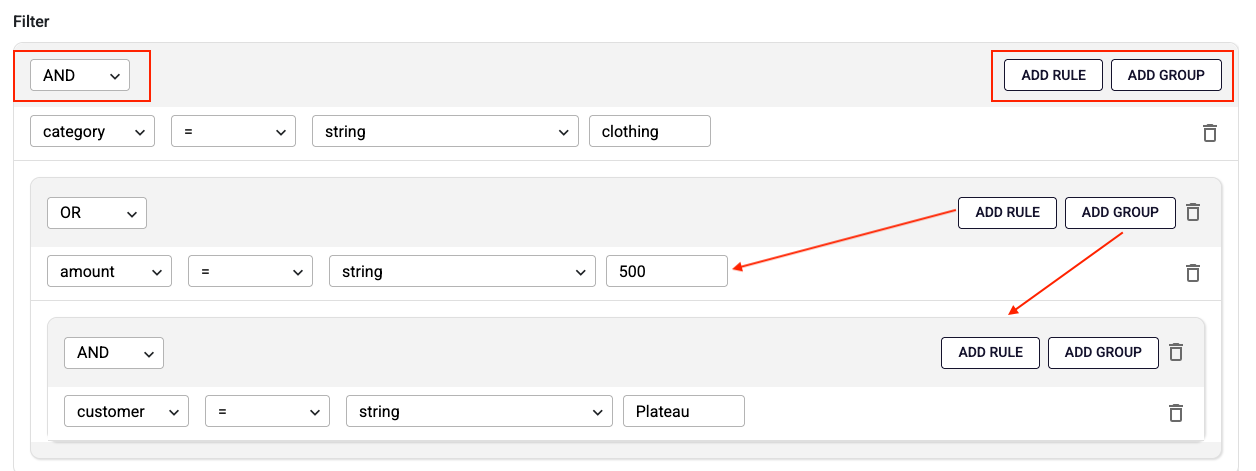
In rule area:
- On the left, you select the attribute from the data.
- On the right, you provide the value to compare against.
- The operator defines how the comparison is made and can be one of the following:"=", "!=", "<", ">", "<=", ">=", "contains", "begins with", "ends with", "does not contain", "does not begin with", "does not end with", "is null", "is not null", "in", "not in", "between", "not between".
How to use Multiple Result - Limit and Offset?
When you enable the Multiple Result switch, the Limit and Offset fields become available at the bottom of the page. These fields are optional and can be used to restrict the number of results or to support pagination in API requests.
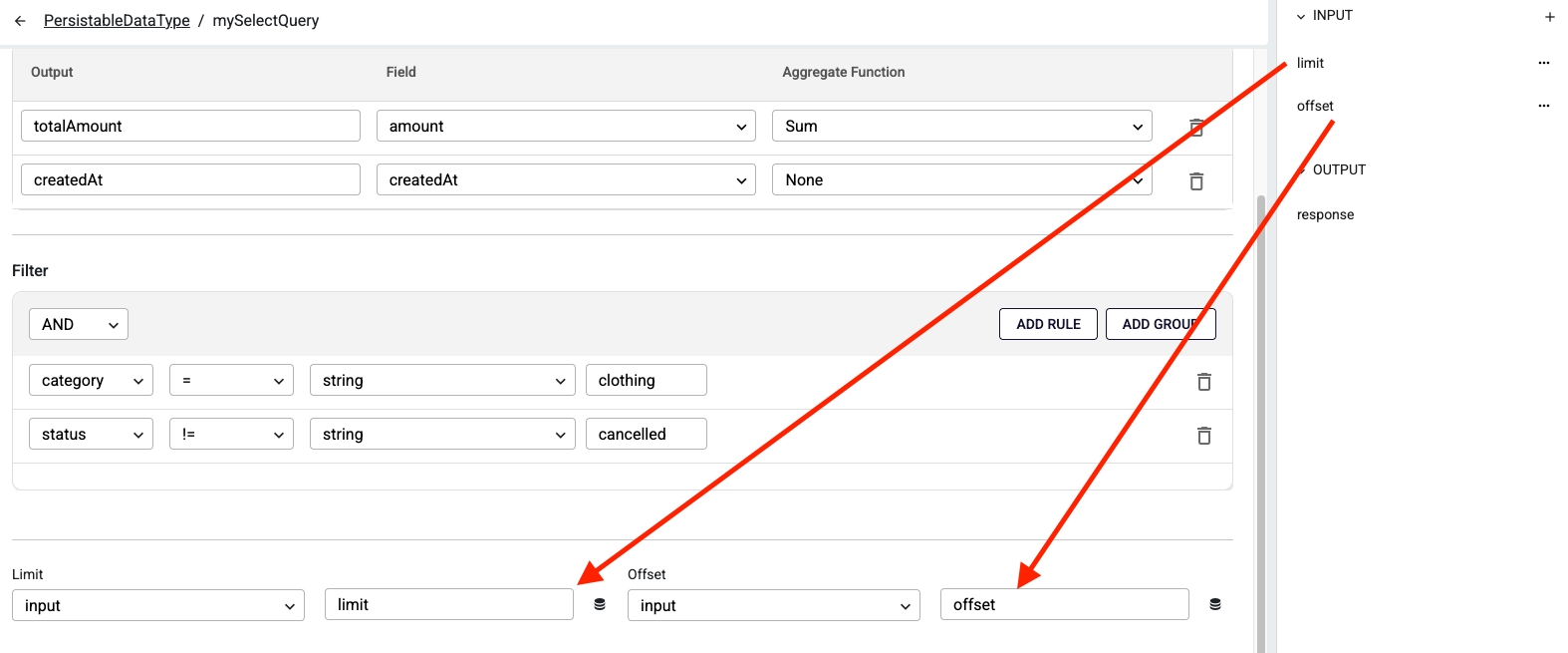
Note: These fields can only be modified through input values, and only when Multiple Result is enabled.
How to add Database Entity in function?
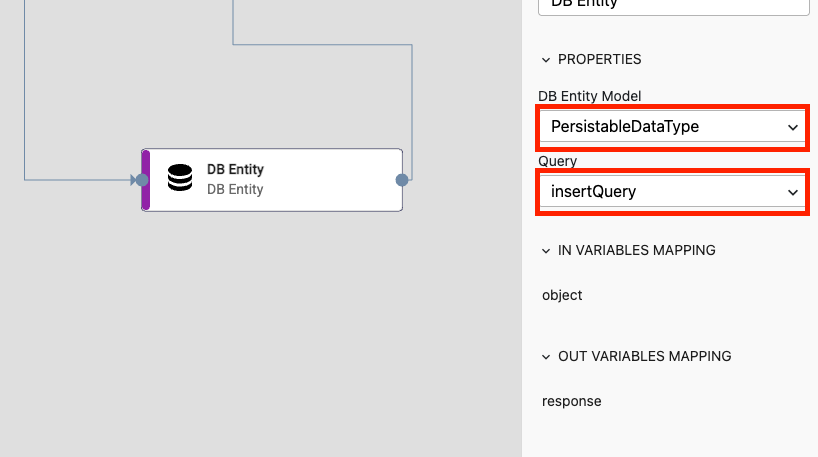
Within a Flow model, you can add a DBEntity step to interact with a persistable data type.
Select the previously created persistable Data Type model as the DB Entity Model.
Below that, choose the query you want to execute.
Based on this selection, the required inputs for the query will change. You can configure these inputs in the IN VARIABLES MAPPING section.
How to use Insert Query?
An Insert query takes an input of type object.
- A new _id is generated to write the object into the database.
- If the object already contains an _id field, it is overridden.
- If not, a new _id is added automatically.
The response of the query is the generated _id of the object, returned as a string.
How to use Delete Query?
A Delete query requires only the _id of the object.
- The record matching this _id is removed from the database.
- The response returns an empty object: {}.
How to use Update Query?
An Update query takes an input of type object, which must include an _id field.
- The record is located based on the provided _id.
- The record is updated with the new values from the object.
- The response returns an empty object: {}.
How to use Select Query?
In a Select query, you can view the inputs defined during query creation.
- There are no default inputs; only the ones you added based on your requirements are available.
- The response is returned as an array.
- If Multiple Result is not enabled, the array contains only a single element.